What is iPaaS (integration platform as a service)?
As a competitive business, it is important to stay up-to-date on the latest technology and the latest solutions available to help your business stay...
Our Business Cloud integration platform suits large and small businesses!
Feel free to contact us to hear how we can help you with integrations (new and old), reporting, budget and forecasting.
+46(0)707 - 81 97 23Read more about what happens at Lundatech, here we gather knowledge and information.

Vår integrationsplattform Business Cloud passar stora som små verksamheter!

Kontakta oss gärna för att höra hur vi kan hjälpa er med integrationer (nya som gamla), rapportering, budget & prognos.
+46(0)707 - 81 97 23Läs mer om vad som händer på Lundatech, här samlar vi kunskap och information.


An integration platform helps businesses connect different systems and applications to create a cohesive and efficient ecosystem. With the right integration platform, companies can automate workflows, improve data sharing, and optimize their processes. In this guide, we cover everything you need to know about integration platforms.
Chapters:
1. What is an integration platform?
2. iPaaS – Integration Platform as a Service
3. Integrations
4. API integrations
5. Integration services
6. Developing an integration strategy
7. Benefits of integration platforms
8. Choosing the right integration platform
9. The future of integration platforms
An integration platform is a software solution that enables connectivity and interoperability between different software systems and applications. These platforms act as a central hub that coordinates and manages data flows between various systems, allowing businesses to eliminate information silos and improve efficiency in their business processes. By using an integration platform, companies can ensure that their different applications and systems communicate seamlessly with each other, leading to better data quality, increased productivity, and improved decision-making.
In today’s digital world, businesses use a variety of applications and systems to manage their operations. Without an integration platform, these systems can become isolated from each other, leading to inefficiencies and data errors. An integration platform solves this problem by connecting these systems and enabling a seamless and accurate flow of data between them. This is especially important to ensure that all departments within a company have access to up-to-date and consistent information, which is crucial for making well-informed business decisions.
One of the most valuable features of an integration platform is the ability to automate workflows. This involves creating and managing workflows that span multiple applications and systems. By automating repetitive and manual tasks, businesses can reduce the risk of human errors, free up employees’ time, and increase overall productivity.
Automate the entire order management process from receipt to delivery by integrating e-commerce platforms with inventory and logistics systems.
Automate hiring processes by integrating recruitment tools with HR systems and background check services.
Data integration is a core function of an integration platform. It ensures that data flows freely and accurately between different systems, eliminating information silos and ensuring that all systems have access to up-to-date and accurate information. This is crucial for improving data quality and enabling a cohesive view of the business.
Integrate CRM systems with marketing and customer service tools to ensure that customer data is consistent and up-to-date across all platforms.
Connect accounting systems with ERP and billing systems to ensure accurate and up-to-date financial reporting.
API management is another critical function of an integration platform. APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) enable direct communication between different systems and applications. By managing and leveraging APIs, businesses can seamlessly and securely connect various systems, enabling customized integrations and enhancing system flexibility.
Use APIs to connect e-commerce platforms with payment gateways, inventory management systems, and delivery tracking services.
Integrate IoT devices with central systems by using APIs to collect and analyze real-time data.
An integration platform is an essential solution for modern businesses looking to optimize their operations and ensure seamless integration between their various systems and applications.
What is iPaaS?
iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service) is a cloud-based solution that facilitates the integration of various applications and services. This type of platform provides a centralized solution for connecting cloud applications, on-premises systems, and data sources without the need for costly and complex infrastructure. With iPaaS, businesses can efficiently manage data flows, automate workflows, and ensure that all systems work seamlessly together.
How does iPaaS work?
iPaaS platforms use a combination of connectors, APIs, and predefined integration modules to link different systems. With a user-friendly interface, businesses can build, monitor, and manage integrations without requiring deep technical expertise. The platform provides tools for visually designing integration flows, making it easy to create and maintain integrations.
One of the biggest advantages of iPaaS is its scalability. Since the platform is cloud-based, it can easily adapt to a company’s needs and growth. This means businesses can start with small-scale integrations and gradually expand without having to worry about rebuilding the infrastructure.
iPaaS platforms can dynamically allocate resources based on current load and demand, ensuring optimal performance regardless of how many integrations are running simultaneously.
Businesses can quickly add new applications and systems to their integration network without needing to make extensive changes to the existing infrastructure.
iPaaS provides a cost-effective integration solution by eliminating the need to invest in and maintain expensive hardware and software. With a subscription-based model, businesses only pay for the resources they use, reducing capital expenditures.
No initial investment:
Since iPaaS is a cloud-based service, there are no upfront costs for hardware or software. Businesses can start using the service immediately and scale up as needed.
Maintenance and updates:
The iPaaS provider manages maintenance and updates, reducing the internal IT workload and ensuring that the platform is always up to date with the latest features and security enhancements.
Another key advantage of iPaaS is its rapid implementation. With preconfigured connectors and templates, businesses can quickly set up integrations and start benefiting from them almost immediately.
Faster Time-to-Market:
By using iPaaS, companies can implement new integrations and launch new services much faster than with traditional integration methods. This gives them a competitive advantage by allowing them to adapt quickly to market changes.
Ease of use:
Many iPaaS solutions offer user-friendly, drag-and-drop interfaces, making it easy for both technical and non-technical users to create and manage integrations without extensive coding.
iPaaS platforms offer a wide range of features and capabilities that make them an attractive solution for businesses looking to streamline their integration processes.
iPaaS enables secure and reliable data transfer between different systems and applications. The platform can also transform data into the required format for each system, ensuring compatibility.
iPaaS provides tools for designing, implementing, and monitoring complex workflows that involve multiple systems and applications. This enables automation of business processes and reduces manual tasks.
iPaaS platforms support API management, making it easy to connect different systems and applications. API management tools help ensure secure and efficient communication between systems.
iPaaS providers offer advanced security features, including data encryption, authentication, and access control, to protect data and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
iPaaS is a powerful and flexible solution for businesses looking to streamline their integration processes and leverage the benefits of cloud technology. With its scalability, cost-effectiveness, and fast implementation, iPaaS is an attractive option for companies of all sizes.

Business Cloud provides you with the integration tools of the future—today. Contact us to learn how Business Cloud can help you with your data needs right away!
Integrations are the key to creating a cohesive ecosystem of applications and services within a company. By integrating different systems and applications, businesses can streamline their processes, improve data quality, and establish a more seamless and connected work environment. Here are some of the most common types of integrations used by businesses:
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems are essential for managing customer data and interactions. By integrating CRM systems with other tools, businesses can gain a holistic view of their customers and enhance their marketing and sales efforts. CRM integrations help ensure that all customer information is centralized and accessible to all relevant departments.
By connecting the CRM system to email marketing tools, businesses can automate email campaigns based on customer data and behaviors. This enables more personalized and relevant messaging, which can increase engagement and conversion rates.
Integrating the CRM system with customer service platforms provides support teams with full access to customer history, improving their ability to handle inquiries quickly and efficiently. This can lead to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
By integrating the CRM system with e-commerce platforms, businesses can track customers’ purchase history and online behavior. This information can be used to personalize marketing campaigns and enhance the customer experience with tailored product recommendations.
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems manage critical business processes such as accounting, procurement, and inventory management. By integrating ERP systems with other business applications, companies can optimize their operational processes and gain better insights into their business. ERP integrations ensure that data flows seamlessly between different business functions, improving efficiency and reducing the risk of errors.
Integrating the ERP system with inventory management systems allows businesses to automate inventory updates, track stock levels in real time, and improve inventory control. This can reduce excess stock levels and lower costs associated with overstocking or stock shortages.
Connecting the ERP system to accounting software ensures that financial transactions are accurately recorded and that financial data is always up to date. This improves the accuracy of financial reporting and simplifies the closing process.
Integrating the ERP system with procurement systems helps streamline purchasing processes, manage supplier relationships, and track purchase orders. This can lead to better-negotiated purchasing prices and improved supply chain management.
Marketing integrations help businesses coordinate their marketing efforts across different channels and platforms, improving efficiency and delivering better results. By integrating marketing tools with other systems, companies can create a more cohesive and data-driven marketing strategy.
By integrating marketing automation tools with social media platforms, businesses can plan, publish, and analyze social media campaigns from a centralized platform. This enables tracking engagement, measuring campaign effectiveness, and adjusting strategies based on insights.
Connect marketing tools to advertising platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads to optimize advertising strategies and track ROI. This helps businesses better understand which campaigns deliver the best results and adjust their advertising efforts accordingly.
Integrate marketing tools with web analytics platforms like Google Analytics to gain insights into website traffic and user behavior. This allows for more informed decisions about website optimization and marketing strategies based on data on how visitors interact with the site.
Beyond the most common integrations, there are many other types of integrations that can be essential depending on a company’s needs and industry. Some examples include:
Integrate HR systems with payroll and time-tracking systems to automate HR processes and ensure accurate payroll management and compliance with labor regulations.
Connect project management tools with time-tracking and resource management systems to enhance project planning and resource allocation.
Integrate customer service tools with ticketing systems and knowledge bases to improve customer support and streamline issue resolution.
Integrations are essential for creating an efficient and cohesive ecosystem of applications and services within a company. By leveraging integration platforms, businesses can ensure that their various systems and applications work seamlessly together, leading to improved efficiency, better data quality, and increased customer satisfaction.
API integrations enable direct communication between different systems and applications by using APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). APIs act as intermediaries that allow various software solutions to interact, exchange data, and perform functions without human intervention. This is one of the most flexible and powerful integration methods, allowing businesses to create customized solutions that precisely match their needs and business processes.
APIs define a set of rules and protocols that allow one application to communicate with another. They provide standardized methods for requesting and transferring data between systems, enabling smooth and efficient integration. An API integration can be simple, such as retrieving data from another application, or complex, involving the orchestration of multiple services to perform a series of actions.
Representational State Transfer (REST) is an architectural style that uses standard HTTP methods and is known for its simplicity and scalability.
Simple Object Access Protocol (SOAP) is a protocol specification for exchanging structured information in web services, known for its security and reliability.
A data query language for APIs and a runtime for executing queries using existing data, offering more flexibility and efficiency in retrieving data.
API integrations offer a high degree of customization, enabling businesses to create tailored solutions that precisely match their specific needs and business processes. By leveraging APIs, companies can develop and implement functionalities specifically designed to support their unique requirements.
APIs enable tailored functionality that can be integrated directly into existing applications, allowing businesses to build solutions that perfectly fit their business models.
APIs provide the flexibility to quickly adapt and modify integrations as business needs evolve, without requiring major overhauls of entire systems.
One of the biggest advantages of API integrations is the ability to ensure data is updated in real-time. This is crucial for many business applications where up-to-date information is necessary for making informed decisions and maintaining operational efficiency.
APIs enable immediate data transfers, ensuring that all systems and applications always have the latest information.
Real-time data exchange reduces the risk of errors caused by outdated information and enhances the accuracy of business decisions.
API integrations can be designed to use secure data transfer methods, protecting sensitive information and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. This is especially important for businesses handling large volumes of customer data or sensitive business information.
APIs can implement strong authentication and authorization mechanisms to ensure that only authorized users and systems have access to data and functionalities.
APIs can use encryption to protect data during transmission, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access.
APIs can include features for tracking and monitoring all activity, helping detect and respond to security threats in real time.
API integrations are used across various industries and scenarios to improve efficiency, enable new functionalities, and enhance user experience. Some common use cases include:
Integrate payment gateways, inventory management systems, and customer relationship management (CRM) tools to create a seamless shopping experience.
Use APIs to connect banking services, accounting software, and investment tools, enabling automated financial processes and improved customer service.
APIs can connect electronic health records (EHRs), laboratory results, and patient scheduling systems to enhance healthcare quality and delivery efficiency.
Despite the many benefits, implementing API integrations comes with challenges that businesses need to be aware of:
Designing and implementing API integrations can be technically complex, requiring a deep understanding of both the source and target applications.
APIs must be continuously maintained and updated to ensure compatibility with evolving systems and security requirements.
Poorly configured APIs can pose security risks, including data breaches and unauthorized access, requiring robust security measures.
By understanding and leveraging the benefits of APIs, businesses can improve their processes, increase efficiency, and create a more integrated and secure IT environment.
An integration service provides specialized expertise and tools for designing, implementing, and maintaining integrations between different systems and applications within a company. These services are essential for ensuring seamless and efficient communication between various business systems, resulting in improved efficiency, better data quality, and more cohesive business processes.
Why are integration services needed?
Integration services are particularly important for businesses that rely on multiple software systems and applications to manage their operations. Without effective integrations, these systems can become isolated from each other, leading to inefficiencies, data errors, and poor decision-making. Integration services ensure that data flows freely and accurately between systems, enhancing overall business performance.
One of the most fundamental services offered by integration providers is consultation. Through consultation, experts help businesses identify and design their integration needs. This includes analyzing existing systems, understanding business processes, and identifying areas where integration can improve efficiency.
Conduct an in-depth assessment of the company’s current systems and processes to identify specific integration needs.
Develop an integration strategy tailored to the company’s business goals and technical requirements.
Provide guidance on the best technical solutions and tools to achieve effective integrations.
The implementation of integrations is a critical phase where integration services leverage their expertise to ensure the seamless and efficient connection of various systems. This step involves setting up, configuring, and testing integrations to ensure they function as expected.
Setting up and configuring systems to enable integrations, including API setup and data connections.
Ensuring data is transferred accurately between systems without loss or corruption.
Conducting rigorous testing to verify that integrations work correctly and meet all business requirements.
Once integrations are implemented, integration services provide ongoing support and maintenance to ensure they continue functioning efficiently without disruptions. This includes monitoring, troubleshooting, and updating integrations as needed.
Continuous tracking of integration flows to detect and resolve any issues in real time.
Rapid identification and resolution of problems to minimize downtime and business impact.
Regular updates and upgrades to ensure integrations remain compatible with new system versions and take advantage of the latest technological advancements.
Integration services offer numerous advantages that help businesses maximize the value of their technology investments and enhance their business processes.
Access to experienced integration specialists with in-depth knowledge and experience in handling complex integration projects.
Faster implementation and problem resolution compared to managing integrations in-house, freeing up internal resources for other business-critical tasks.
Reduce integration costs by leveraging a service with specialized tools and processes for efficiently managing integration projects.
Integration services can scale up or down based on business needs, making them a flexible solution that adapts to changing business requirements.
Integration services are used across various industries and scenarios to ensure smooth and efficient system communication.
Integrate e-commerce platforms with payment systems, inventory management, and CRM to create a seamless customer experience.
Connect electronic health records, laboratory data systems, and patient management systems to improve healthcare delivery.
Use integrations to connect banking services, accounting software, and investment tools to streamline financial processes and enhance customer service.
Integration services play a crucial role in helping businesses manage and optimize their technology ecosystems. By providing specialized expertise and tools to design, implement, and maintain integrations, these services ensure that a company’s systems work together efficiently and cohesively. This leads to improved business efficiency, better data quality, and more informed decision-making.
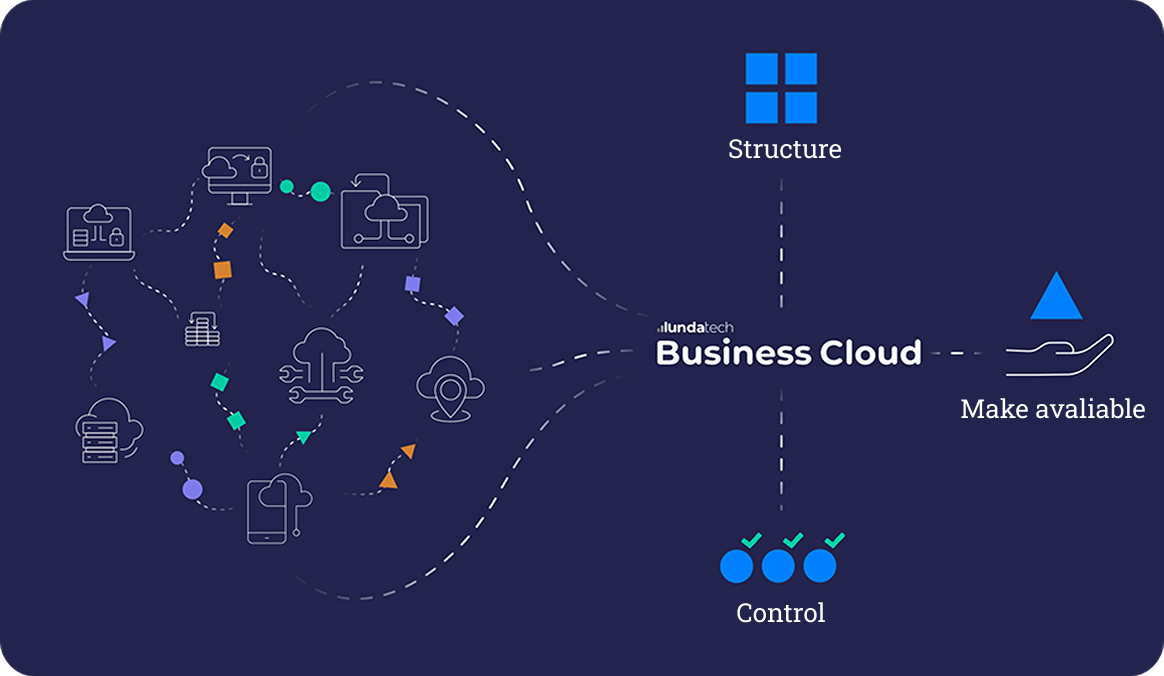
Creating an effective integration strategy is essential to ensure that all systems and applications work seamlessly together. A well-developed integration strategy enables efficient data sharing, improved operational efficiency, and a cohesive user experience. Here is a step-by-step guide to developing a robust integration strategy.
The first step in developing an integration strategy is to identify the needs. This involves mapping out the systems and applications that need to be integrated and understanding how they are currently used within the organization. It is essential to involve key stakeholders from different departments to get a holistic view of the integration requirements.
Conduct an inventory of all existing systems and applications within the organization that require integration. This includes both internal systems and external services.
Determine which data needs to be transferred between systems and which business processes are affected by these data flows.
Understand the specific needs and challenges each system and department faces regarding integration.
After identifying the needs, the next step is to evaluate and select the tools and platforms that best meet those requirements. There are many integration tools and platforms available on the market, and it is crucial to choose those that best fit the organization’s specific demands and technical environment.
Explore different integration technologies such as API integrations, middleware, and iPaaS (Integration Platform as a Service). Assess the advantages and disadvantages of each approach in relation to your needs.
Ensure that the selected tools are compatible with existing systems and can scale as the business grows.
Analyze the costs of different tools and platforms and compare them with the potential return on investment.
With the right tools selected, the next step is to create a detailed plan and design for the integrations. This involves developing a technical blueprint that outlines how integrations will be executed and how different systems will be connected.
Create a detailed technical design specifying how integrations will be implemented, including data flows, API calls, and security measures.
Develop a project plan outlining the different phases of the integration project, including timelines, resources, and milestones.
Identify potential risks that may impact the integration project and develop mitigation plans to address these risks.
Once planning and design are complete, it’s time to execute the integrations and test them to ensure they function correctly. This step includes setting up the integrations, conducting tests, and verifying that all systems work smoothly together.
Carry out the integrations according to the technical design. This includes configuring APIs, setting up data connections, and implementing workflows.
Perform comprehensive testing to verify that the integrations work as expected. This includes functional testing, performance testing, and security testing.
Identify and resolve any issues discovered during testing and make necessary adjustments to ensure optimal functionality.
After implementation, it is essential to continuously monitor the performance of the integrations and make necessary adjustments to optimize their efficiency. This step involves using monitoring tools to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
Use monitoring tools to continuously track the performance of integrations. This includes monitoring data flows, system load, and response times.
Identify and implement improvements to optimize integration performance. This may include adjusting configurations, updating APIs, and refining workflows.
Ensure that integrations remain updated and maintained to accommodate changes in systems and business processes.
Improved business process efficiency through automated data flows and seamless system communication.
Enhanced data quality by eliminating manual data transfers and ensuring data consistency and accuracy.
Increased flexibility to adapt to changes in business needs and technological requirements through a scalable and adaptable integration solution.
Reduced need for manual processes and duplicate work, leading to long-term cost savings.
Access to up-to-date and accurate data enables better and more informed business decisions.
A robust integration strategy is essential to ensure that all systems and applications within an organization work together seamlessly, leading to improved business operations and increased competitiveness.
Integration platforms offer numerous advantages for businesses looking to connect their systems and optimize their processes. By utilizing an integration platform, companies can improve efficiency, ensure data quality, reduce costs, and enhance the customer experience. Here’s a closer look at the key benefits:
One of the most significant benefits of integration platforms is the increased efficiency achieved through automation and workflow optimization. By eliminating manual processes and ensuring smooth data flow between systems, businesses can save time and resources.
Integration platforms enable the automation of repetitive and manual tasks, reducing the risk of human errors and allowing employees to focus on more strategic activities.
Ensuring that information is transferred quickly and efficiently between systems helps businesses accelerate their operations and reduce lead times.
Many integration platforms offer a centralized dashboard to manage and monitor all integrations, providing better control and oversight of business processes.
Integration platforms ensure that data transferred between different systems is accurate, consistent, and up-to-date. This is essential for making informed business decisions and maintaining high data integrity within the organization.
By ensuring that data is entered once and then shared across systems, integration platforms minimize the risk of duplication and inconsistencies.
Integration platforms ensure that all systems and departments have access to the latest information, keeping the organization synchronized and efficient.
Many integration platforms offer data validation tools that help identify and correct errors before they impact business processes.
By eliminating manual processes and improving efficiency, integration platforms lead to significant cost savings for businesses, including both direct and indirect costs.
Automation of repetitive tasks minimizes the need for additional staff, leading to lower personnel costs.
Optimized workflows ensure resources are used efficiently, reducing waste and maximizing return on investment.
Integration platforms reduce the need for extensive internal IT resources to manage integrations, decreasing IT support and maintenance costs.
Another key benefit of integration platforms is the improved customer experience, achieved by ensuring a seamless and connected user journey. This is crucial for building customer loyalty and driving business growth.
By making customer data available and up-to-date in real-time, businesses can provide faster and more relevant responses to customer inquiries and needs.
Integration platforms enable businesses to collect and analyze data from multiple sources, allowing them to personalize offers and communication for each customer.
By integrating various customer-related systems (such as CRM, e-commerce, and customer service), companies can offer a consistent experience across all touchpoints, enhancing overall customer satisfaction.
Integration platforms enhance business agility by enabling quick adaptation to changing business needs and market conditions. This is particularly important in today’s fast-paced business environment.
With an integration platform, businesses can quickly and easily add new applications and systems to their ecosystem without extensive redevelopment.
Integration platforms allow businesses to tailor their integration solutions to evolving needs, offering greater flexibility and scalability.
By enabling fast and seamless integration of new technologies and solutions, integration platforms help businesses drive innovation and stay competitive.
Integration platforms provide businesses with access to real-time data and insights, improving decision-making and enabling better, more informed choices.
By aggregating data from multiple sources and systems in real-time, integration platforms provide businesses with an up-to-date and holistic view of their operations.
Advanced analytics and reporting tools help businesses identify trends, patterns, and opportunities for improvement.
With access to accurate and up-to-date data, businesses can make data-driven decisions that enhance performance and reduce the risk of errors.
Integration platforms offer a wide range of benefits that help businesses optimize processes, improve data quality, reduce costs, and create better customer experiences. By leveraging an integration platform, companies can ensure that their systems and applications work seamlessly together, leading to increased efficiency and competitiveness.
Selecting the right integration platform is crucial to maximizing benefits and ensuring a smooth implementation. A well-chosen platform can help businesses efficiently manage their integrations, streamline processes, and achieve their business goals. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing an integration platform.
One of the most important aspects to consider is the platform’s functionality. It is essential that the platform offers the features and capabilities required to meet the company’s integration needs.
Ensure that the platform can handle various types of integrations, including API integrations, data transfers, and workflow automation.
Evaluate whether the platform is compatible with the systems and applications the company already uses, including both cloud-based and on-premises solutions.
Check if the platform allows customization to meet specific business needs, such as tailored integration solutions and flexible configurations.
A user-friendly platform is essential for ensuring a quick and smooth implementation. It is important that both technical and non-technical users can use the platform efficiently.
Choose a platform with an intuitive and user-friendly interface that makes it easy to configure and manage integrations.
The platform should be easy to learn and use, with clear instructions and documentation that facilitate adoption.
Many modern integration platforms offer drag-and-drop features for visually creating and configuring integrations, simplifying the process significantly.
The cost of an integration platform is an important factor, especially for small and medium-sized businesses. Finding a platform that fits the budget without compromising essential features is crucial.
Evaluate the platform’s pricing model, including licensing fees, subscription costs, and any additional charges for extra features or support.
Ensure that the cost scales with the business’s growth. The platform should offer flexible pricing models that allow businesses to pay only for the features and resources they use.
An integration platform is only as good as the support that comes with it. It is essential to ensure that the platform provides sufficient support and resources to assist with troubleshooting and maintenance.
Evaluate the different support options available, including phone, email, and chat support. Ensure that 24/7 support is available if needed.
The platform should provide comprehensive documentation, guides, and training materials to help users understand and use the platform effectively.
An active user community and discussion forums can be valuable for sharing experiences, troubleshooting issues, and gaining insights from other users.
It is important to choose an integration platform that can grow with the business and handle increased performance and capacity demands.
The platform should offer a scalable infrastructure that can handle increasing data volumes and users without affecting performance.
Check if the platform provides performance guarantees, such as response times and uptime, to ensure it meets business needs.
The platform should allow easy expansion of capacity and functionality as the company’s needs evolve.
Security is a critical factor when selecting an integration platform, especially for businesses that handle sensitive information and mission-critical data.
The platform should offer strong data encryption to protect information during transfer and storage.
Ensure that the platform has robust access control mechanisms to restrict data and functionalities to authorized users only.
The platform should comply with relevant regulatory standards such as GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2 to ensure data is handled securely.
Choosing the right integration platform is a crucial investment for businesses looking to optimize their processes and ensure seamless system and application integration. By carefully considering factors such as functionality, usability, cost, support, scalability, and security, businesses can find a platform that best meets their needs and helps them achieve their goals. A well-chosen integration platform can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance user experience, ultimately leading to greater competitiveness and business success.
Integration platforms are continuously evolving, offering new opportunities for businesses to enhance their processes and improve efficiency. As technology advances, integration platforms will play an increasingly vital role in enabling seamless communication between different systems and applications.
Here are some of the key trends and future developments shaping the future of integration platforms.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) will have a significant impact on the future of integration platforms. These technologies can improve and automate integrations, making them more efficient and reliable.
AI and ML can automatically detect and map data relationships between different systems, reducing manual work and minimizing errors.
Machine learning can be used to predict and identify potential issues before they occur, enabling proactive problem-solving and improved system reliability.
AI-driven platforms can optimize workflows based on past data analysis and usage patterns, leading to more efficient processes and better resource utilization.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing how businesses collect and use data. Future integration platforms will need to manage the increasing volume of data from IoT devices and ensure seamless integration with business applications.
IoT devices generate massive amounts of real-time data, and integration platforms must process and analyze this data quickly to enable real-time decision-making and automation.
IoT integrations require robust security measures to protect sensitive data and scalable infrastructures to handle the growing volume of connected devices.
IoT data must be integrated with existing business systems, such as ERP and CRM, to provide a comprehensive view of operations and enable data-driven decision-making.
With the rise of both cloud-based and on-premises systems, businesses need a hybrid integration strategy to ensure seamless connectivity across different environments. Hybrid integrations combine the best of cloud technology and on-premises systems to create a flexible and efficient integration solution.
Hybrid integrations allow businesses to choose the best solutions for their specific needs, whether cloud-based or on-premises, providing greater flexibility.
By combining cloud-based and on-premises systems, businesses can optimize costs by leveraging cloud services for scalability while maintaining critical business functions on-premises.
Hybrid integrations ensure smooth data transfer between cloud-based and on-premises systems, providing a unified view of data and business processes.
Edge computing involves processing data near the source—where the data is generated—rather than sending it to a central server or cloud for processing. This reduces latency and improves performance for integrations that require fast response times.
Integration platforms can leverage edge computing to process data locally, reducing the burden on central systems and improving response times.
Blockchain technology offers a secure and transparent method for managing data transfers and transactions. Integration platforms can leverage blockchain to ensure data integrity and security in integration processes.
Blockchain can be used to create immutable records of data transfers, ensuring that data is not tampered with or lost during transmission.
Blockchain enables decentralized integrations where data can be transferred and validated without a central authority, enhancing security and reliability.
With increasing regulations and data security requirements, future integration platforms will need to provide advanced security features and compliance support.
Future integration platforms will have built-in security functionalities such as data encryption, authentication, and authorization to protect data during transmission and storage.
Platforms will offer tools and features to ensure compliance with global and local data protection regulations, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and CCPA.
The future of integration platforms looks promising, with many exciting advancements and trends shaping how businesses manage their integrations. By leveraging AI and machine learning, integrating IoT devices, adopting hybrid integrations, and focusing on edge computing, blockchain, and data security, companies can develop more efficient and secure integration solutions. These innovations will enable seamless system communication, improve business processes, and provide companies with a competitive edge in an increasingly high-tech and fast-changing world.


As a competitive business, it is important to stay up-to-date on the latest technology and the latest solutions available to help your business stay...

How do we ensure our data quality? This is an ever-present point of discussion in many companies, regardless of department or duties. The quality of...

How do we ensure our data quality? This is an ever-present point of discussion in many companies, regardless of department or duties. Data quality...